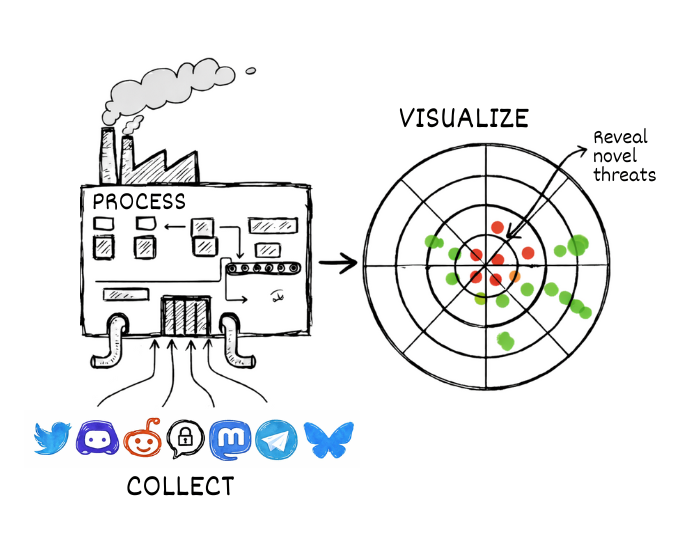
About
Cybersecurity professionals and researchers are continually challenged by the rapid pace at which new cyber threats and defense techniques emerge. Traditional channels for information dissemination—academic publications, industry reports, CVE databases—often lag behind real-time discussions happening across social platforms. CYBERSNIPE addresses this gap by leveraging state-of-the-art NLP and signal detection techniques to identify emerging themes, tools, and threats before they reach mainstream coverage.
We’re likely to see more novel exploits and vulnerabilities as large language models continue to get exponentially smarter. Research from Anthropic shows that frontier AI models can both rapidly exploit known vulnerabilities at scale and independently discover novel zero-day flaws.
AI-2027 research suggests AI cyber capabilities may be improving at superexponential rates. In this environment, staying current with the latest threats is no longer a best practice but a requirement.
System Architecture
CYBERSNIPE is a two-service architecture: a FastAPI backend (Python) for processing and an Astro frontend (TypeScript) for visualization. Custom scrapers and ingestion methods POST raw data to the FastAPI service, which processes everything and exposes a JSON API consumed by the frontend.
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ COLLECTION LAYER │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │
│ │ Twitter │ │ Telegram │ │ Discord │ │ Reddit │ │ Custom │ │
│ │ Scraper │ │ Bot │ │ Bot │ │ Scraper │ │ Scrapers │ │
│ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┴──────┬──────┴─────────────┴─────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ POST /api/ingest │
└────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ FASTAPI BACKEND (Python) │
│ github.com/yourorg/cybersnipe-api │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ /api/ingest ← Receives raw posts from any scraper │ │
│ │ /api/snipes ← Returns all processed snipes with radar scores │ │
│ │ /api/tags ← Returns tag registry with momentum/impact │ │
│ │ /api/health ← Health check for monitoring │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ Processing Pipeline: │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │
│ │ BERTopic │→ │ NER │→ │ Match │→ │ Momentum │→ │ Impact │ │
│ │ Extract │ │ Entities │ │ Tags │ │ Calc │ │ Score │ │
│ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ │
│ │
│ Storage: PostgreSQL (snipes, tags) + Redis (cache, rate limits) │
└──────────────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
GET /api/snipes
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ASTRO FRONTEND (TypeScript) │
│ github.com/yourorg/cybersnipe-web │
│ (this repository) │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Fetches /api/snipes → Renders Radar visualization │ │
│ │ Fetches /api/tags → Renders tag list with scores │ │
│ │ Static generation at build time OR client-side fetch │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘⊹ Collect
Custom scrapers and bots continuously monitor conversations across Twitter/X, Telegram, Discord, Reddit, security forums, and private group chats. Each scraper is independent and can be implemented in any language—the only requirement is that they POST to the FastAPI ingestion endpoint.
Example scrapers might include:
- Python script using
tweepyfor Twitter/X - Telegram bot using
python-telegram-bot - Discord bot using
discord.py - Selenium/Playwright scrapers for forums
- RSS feed parsers for security blogs
All scrapers POST to the same endpoint regardless of implementation.
⊹ Process (FastAPI Backend)
The FastAPI backend is the central processing hub. It’s a separate repository/service that handles all NLP, scoring, and data storage.
FastAPI Service Structure
# main.py - FastAPI application entry point
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Optional
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(
title="CYBERSNIPE API",
description="Threat intelligence processing pipeline",
version="1.0.0"
)
# ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
# REQUEST/RESPONSE MODELS
# ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
class IngestPayload(BaseModel):
"""Schema for incoming posts from any scraper"""
content: str # Full text of the post
source: str # "twitter" | "telegram" | "discord" | "reddit" | "forum"
author: str # Username or identifier
timestamp: datetime # When the post was created
url: Optional[str] = None # Original source URL
channel: Optional[str] = None # Channel/group name
thread_id: Optional[str] = None # Parent thread if reply
reply_to: Optional[str] = None # ID of message being replied to
engagement: Optional[dict] = None # {"likes": 0, "shares": 0, "replies": 0}
class IngestResponse(BaseModel):
"""Response after processing a post"""
success: bool
snipe_id: str # Unique ID for this snipe
tags_extracted: list[str] # Topics found in the post
tags_matched: list[str] # Existing tags this linked to
tags_created: list[str] # New tags created
momentum_updates: list[dict] # Tags whose momentum changed
class TagResponse(BaseModel):
"""Schema for tag data"""
tag: str
segment: str
segment_label: str
mention_count: int
momentum: float # 0-1 normalized
impact: str # "none" | "very_low" | ... | "very_high"
impact_value: float # 0-1 numeric
confidence: float # 0-1
last_mentioned: datetime
burst_score: float # Kleinberg burst indicator
class SnipeResponse(BaseModel):
"""Schema for processed snipe"""
id: str
title: str
content: str
source: str
author: str
url: Optional[str]
pub_date: datetime
tags: list[TagResponse]
radar: dict # {confidence, momentum, maxImpact, primarySegment}
# ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
# ENDPOINTS
# ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
@app.post("/api/ingest", response_model=IngestResponse)
async def ingest_post(payload: IngestPayload):
"""
Main ingestion endpoint. Any scraper POSTs here.
Processing steps:
1. Extract topics via BERTopic
2. Extract entities via NER (CVEs, malware names, etc.)
3. Match to existing tags or create new ones
4. Recalculate momentum for all affected tags
5. Update confidence scores
6. Store snipe in database
7. Return processing results
"""
# ... processing logic ...
pass
@app.get("/api/snipes", response_model=list[SnipeResponse])
async def get_snipes(
limit: int = 100,
offset: int = 0,
segment: Optional[str] = None,
min_momentum: Optional[float] = None,
min_impact: Optional[str] = None,
since: Optional[datetime] = None
):
"""
Returns processed snipes with all radar scores.
This is what the Astro frontend fetches.
"""
# ... query logic ...
pass
@app.get("/api/tags", response_model=list[TagResponse])
async def get_tags(
segment: Optional[str] = None,
min_momentum: Optional[float] = None
):
"""
Returns the tag registry with current scores.
Used to populate the radar visualization.
"""
# ... query logic ...
pass
@app.get("/api/health")
async def health_check():
"""Health check for monitoring/load balancers"""
return {"status": "healthy", "timestamp": datetime.utcnow()}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)Posting Data to FastAPI
Any scraper can POST to the ingestion endpoint. Here are examples in different languages:
Python (requests)
import requests
from datetime import datetime
response = requests.post(
"https://api.cybersnipe.ch/api/ingest",
json={
"content": "New LockBit 4.0 variant targeting healthcare systems via RDP exploitation",
"source": "twitter",
"author": "security_researcher_42",
"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
"url": "https://twitter.com/...",
"channel": "infosec",
"engagement": {"likes": 142, "shares": 89, "replies": 23}
},
headers={"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"}
)
print(response.json())
# {
# "success": true,
# "snipe_id": "snp_a1b2c3d4",
# "tags_extracted": ["lockbit", "ransomware", "healthcare", "rdp"],
# "tags_matched": ["lockbit", "ransomware", "rdp"],
# "tags_created": [],
# "momentum_updates": [
# {"tag": "lockbit", "old": 0.45, "new": 0.48},
# {"tag": "ransomware", "old": 0.92, "new": 0.93}
# ]
# }JavaScript/Node.js (fetch)
const response = await fetch("https://api.cybersnipe.ch/api/ingest", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
content: "Critical RCE vulnerability in Apache Struts CVE-2024-XXXX",
source: "reddit",
author: "u/vuln_hunter",
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
url: "https://reddit.com/r/netsec/...",
channel: "r/netsec",
}),
});
const result = await response.json();
console.log(result.tags_extracted); // ["rce", "apache", "struts", "cve-2024-xxxx"]cURL (shell scripts)
curl -X POST https://api.cybersnipe.ch/api/ingest \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"content": "APT29 using new supply chain attack vector via npm packages",
"source": "telegram",
"author": "threat_intel_group",
"timestamp": "2026-01-25T14:30:00Z",
"channel": "APT Tracking"
}'Processing Pipeline Details
2. Topic Extraction via BERTopic
We use BERTopic (Grootendorst, 2022) for dynamic topic modeling. BERTopic combines:
- Sentence-BERT embeddings (Reimers & Gurevych, 2019) for semantic document representation
- UMAP dimensionality reduction (McInnes et al., 2018) to preserve local structure
- HDBSCAN clustering (Campello et al., 2013) for density-based topic discovery
- c-TF-IDF for interpretable topic representations
This approach can discover topics like “AI-Assisted Phishing”, “CAPTCHA Bypassing with CVE-2024-XXXX”, or “Credential Harvesting via Telegram Bots” without predefined categories.
For cybersecurity-specific understanding, we fine-tune on SecureBERT (Aghaei et al., 2022), a BERT model pre-trained on cybersecurity text corpora including CVE descriptions, security blogs, and threat reports.
3. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
We extract structured entities using a fine-tuned NER model trained on cybersecurity corpora:
| Entity Type | Examples |
|---|---|
CVE_ID | CVE-2024-3400, CVE-2023-44487 |
MALWARE | LockBit, BlackCat, Emotet |
THREAT_ACTOR | APT29, Lazarus Group, FIN7 |
TOOL | Cobalt Strike, Mimikatz, Metasploit |
TECHNIQUE | credential stuffing, SQL injection, DLL sideloading |
PLATFORM | AWS, Kubernetes, Solana |
This is based on approaches from CyNER (Alam et al., 2022) and extended with custom training data.
4. Topic Linking & Semantic Similarity
New topics are matched against our existing tag registry using a multi-stage process:
- Exact Match: Direct string match against slugified tags (
ransomware,zero-day,flash-loan) - Semantic Similarity: Cosine similarity on Sentence-BERT embeddings. Topics scoring >0.85 link to existing tags.
- Hierarchical Clustering: Related topics are grouped (e.g., “LockBit 3.0” → “LockBit” → “Ransomware”)
- New Tag Creation: Novel topics with no strong match become candidates, pending confidence threshold
This mirrors approaches in Few-shot Learning for Cybersecurity where limited labeled data requires transfer learning.
5. Segment Classification
Every tag maps to one of 8 threat segments:
| Segment | Example Topics |
|---|---|
| Ransomware & Malware | LockBit 4.0, Akira ransomware, Emotet resurgence |
| Zero-Days & CVEs | CVE-2024-3400 (PAN-OS), HTTP/2 Rapid Reset |
| DeFi & Smart Contracts | Flash loan arbitrage, Reentrancy in Uniswap forks |
| Phishing & Social Eng | AI-generated voice phishing, QR code phishing |
| Cloud | AWS IAM privilege escalation, K8s RBAC bypass |
| Supply Chain | npm typosquatting, PyPI malware, XZ Utils backdoor |
| AI & LLM Exploits | Prompt injection, Model poisoning, Jailbreaks |
| Data Breaches | Credential dumps, Database exposures |
Classification uses zero-shot classification via entailment models, allowing new segments without retraining.
6. Momentum & Burst Detection (Trading-Inspired Signals)
We adapt quantitative trading techniques to detect “breakout” topics:
Kleinberg’s Burst Detection (Kleinberg, 2002): Identifies statistically significant increases in mention frequency using a hidden Markov model with exponential inter-arrival times. A topic “bursts” when its mention rate exceeds the expected baseline by a significance threshold.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) Crossover: Borrowed from trading, we compute short-term (4h) and long-term (24h) EMAs of mention counts:
momentum_signal = EMA_4h / EMA_24hWhen momentum_signal > 1.5, a topic is flagged as “hot” (similar to a golden cross in trading).
Z-Score Anomaly Detection: For each topic, we maintain a rolling 7-day baseline and compute:
z_score = (current_mentions - rolling_mean) / rolling_stdTopics with z_score > 2.5 are flagged as anomalous spikes.
Rate of Change (ROC): Similar to price momentum in trading:
ROC = (mentions_today - mentions_7d_ago) / mentions_7d_ago × 100These signals combine into a composite Momentum Score (0–1):
momentum = 0.4 × burst_score + 0.3 × ema_signal + 0.2 × z_score_norm + 0.1 × roc_norm7. Impact Scoring via Threat Intelligence
Potential Impact is determined independently of momentum (a quiet topic can still be critical):
Two-Tier Scoring:
- Segment Base Impact: Inherent risk level (e.g.,
supply_chain→very_high) - Tag-Specific Override: Granular adjustments (e.g.,
typosquatting→low)
CVSS Integration: For CVE-tagged topics, we fetch CVSS scores from NVD and map:
- CVSS 9.0–10.0 →
very_high - CVSS 7.0–8.9 →
high - CVSS 4.0–6.9 →
medium - CVSS 0.1–3.9 →
low
Sentiment & Urgency Analysis: Using FinBERT-style fine-tuning adapted for security context, we detect urgency markers:
- “actively exploited in the wild” → urgency boost
- “proof of concept released” → impact increase
- “patch available” → impact decrease
Impact follows a stoplight color scheme:
none(0.0) → Greenvery_low(0.2) → Limelow(0.4) → Yellowmedium(0.6) → Orangehigh(0.8) → Redvery_high(1.0) → Dark Red
8. Topic Propagation & Graph Dynamics
When new content is ingested:
- Tag Matching: Extract topics, match to existing tags
- Increment Counts: Each matching tag’s
mentionCountincreases - Recalculate Momentum: All momentum scores recompute (max count may have changed)
- Update Timestamps: Tag’s
latestDateupdates to new post’s timestamp - Propagate to Related Posts: All posts sharing these tags receive updated scores
This means a single new post can shift the radar position of multiple older posts. The system models topic dynamics as a weighted graph where edges represent co-occurrence, and PageRank-style propagation distributes “heat” through the network.
⊹ Visualize (Astro Frontend)
The frontend is this website—an Astro/TypeScript application that fetches processed data from the FastAPI backend and renders the Radar visualization.
Frontend ↔ Backend Integration
The Astro frontend fetches data from FastAPI endpoints:
At Build Time (SSG) or Runtime (SSR)
// src/lib/api.ts - API client for FastAPI backend
const API_BASE = import.meta.env.PUBLIC_API_URL || "https://api.cybersnipe.ch";
export interface Snipe {
id: string;
title: string;
content: string;
source: string;
pub_date: string;
tags: Tag[];
radar: {
confidence: number;
momentum: number;
maxImpact: string;
primarySegment: string;
};
}
export interface Tag {
tag: string;
segment: string;
mention_count: number;
momentum: number;
impact: string;
confidence: number;
}
export async function fetchSnipes(options?: {
limit?: number;
segment?: string;
minMomentum?: number;
}): Promise<Snipe[]> {
const params = new URLSearchParams();
if (options?.limit) params.set("limit", String(options.limit));
if (options?.segment) params.set("segment", options.segment);
if (options?.minMomentum)
params.set("min_momentum", String(options.minMomentum));
const response = await fetch(`${API_BASE}/api/snipes?${params}`);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error("Failed to fetch snipes");
return response.json();
}
export async function fetchTags(): Promise<Tag[]> {
const response = await fetch(`${API_BASE}/api/tags`);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error("Failed to fetch tags");
return response.json();
}Astro Page Fetching Data
---
// src/pages/radar/index.astro
import { fetchTags } from "../../lib/api";
import ThreatRadar from "../../components/ThreatRadar.astro";
// Fetch at build time (SSG) or request time (SSR)
const tags = await fetchTags();
// Transform to radar format
const radarData = tags.map(tag => ({
id: tag.tag,
label: tag.tag,
segment: tag.segment,
confidence: tag.confidence,
impact: tag.impact,
momentum: tag.momentum,
mentionCount: tag.mention_count,
}));
---
<ThreatRadar trends={radarData} />Client-Side Reactive Updates (Optional)
// For real-time updates without page refresh
// src/components/RadarLive.tsx (React island)
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { fetchTags, type Tag } from "../lib/api";
export default function RadarLive() {
const [tags, setTags] = useState<Tag[]>([]);
useEffect(() => {
// Initial fetch
fetchTags().then(setTags);
// Poll every 30 seconds for updates
const interval = setInterval(() => {
fetchTags().then(setTags);
}, 30000);
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, []);
return <RadarVisualization data={tags} />;
}Coordinate Mapping
| Visual Property | Data Source | Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Angle (wedge) | segment | 360° ÷ 8 segments = 45° each |
| Radius | confidence | High confidence → center; Low → edge |
| Color | impact | Stoplight palette (green → red) |
| Pulse Animation | momentum | ≥75% momentum triggers pulse |
Confidence Calculation
Confidence represents signal-to-noise certainty (calculated by FastAPI):
confidence = 0.15 + (source_diversity × 0.3) + (author_authority × 0.2) + (momentum × 0.2) + (corroboration × 0.15)Where:
source_diversity: Number of unique platforms discussing the topicauthor_authority: PageRank-style score based on author’s historical accuracycorroboration: Whether multiple independent sources confirm the topic
Trending Topics Ranking
For the homepage “Trending Topics” section, posts are scored using a weighted formula inspired by Hacker News ranking:
score = (avgMomentum × 0.60) + (maxImpact × 0.35) + (recencyScore × 0.05)Recency uses exponential decay:
recencyScore = exp(-λ × hours_since_publish)Where λ controls decay rate (faster decay surfaces newer content).
FastAPI Response Format
The /api/snipes endpoint returns the full scored dataset that the frontend consumes:
{
"meta": { "totalSnipes": 47, "generatedAt": "..." },
"segments": [...],
"impactLevels": [...],
"snipes": [
{
"id": "snp_a1b2c3d4",
"title": "AI-Assisted Phishing Campaign Targeting Fortune 500",
"content": "New campaign using GPT-generated emails...",
"source": "twitter",
"author": "threat_researcher",
"pub_date": "2026-01-25T14:30:00Z",
"radar": {
"confidence": 78,
"momentum": 82,
"maxImpact": "high",
"primarySegment": "social_engineering"
},
"tags": [
{
"tag": "ai-phishing",
"segment": "social_engineering",
"impact": "high",
"momentum": 82,
"mention_count": 47,
"burst_score": 0.91
}
]
}
]
}Deployment Architecture
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PRODUCTION │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ FastAPI Backend Astro Frontend │
│ ───────────────── ────────────── │
│ Host: Railway / Render / Fly.io Host: Vercel / Netlify │
│ URL: api.cybersnipe.ch URL: cybersnipe.ch │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ FastAPI │◄──── fetch ───────│ Astro │ │
│ │ + Uvicorn │ │ (SSG/SSR) │ │
│ └──────┬──────┘ └─────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ PostgreSQL │ │ Redis │ │
│ │ (Neon/ │ │ (Upstash) │ │
│ │ Supabase) │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Scrapers (run anywhere - VPS, Lambda, local machines)
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Twitter │ │ Telegram │ │ Discord │ │ Forum │
│ Scraper │ │ Bot │ │ Bot │ │ Scraper │
└────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ │ │ │
└────────────┴─────┬──────┴────────────┘
│
POST /api/ingest
│
▼
api.cybersnipe.chEnvironment Variables
FastAPI Backend (.env)
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:pass@host:5432/cybersnipe
REDIS_URL=redis://default:pass@host:6379
API_KEYS=key1,key2,key3 # For scraper authentication
HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN=hf_xxx # For SecureBERT modelsAstro Frontend (.env)
PUBLIC_API_URL=https://api.cybersnipe.chResearch References
Key papers informing this methodology:
- BERTopic: Grootendorst, M. (2022). BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure
- SecureBERT: Aghaei, E. et al. (2022). SecureBERT: A Domain-Specific Language Model for Cybersecurity
- Sentence-BERT: Reimers, N. & Gurevych, I. (2019). Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks
- Burst Detection: Kleinberg, J. (2002). Bursty and Hierarchical Structure in Streams
- CyNER: Alam, M. et al. (2022). CyNER: A Python Library for Cybersecurity Named Entity Recognition
- Zero-Shot Classification: Yin, W. et al. (2019). Benchmarking Zero-shot Text Classification
- UMAP: McInnes, L. et al. (2018). UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection
- FinBERT: Araci, D. (2019). FinBERT: Financial Sentiment Analysis with Pre-trained Language Models
The ultimate goal: reveal novel threats before they become widespread incidents.
Questions or feedback? Reach out via email.